 Swipe for more categories
Swipe for more categories 
How Do Electric Cars Perform in the Cold Weather?
How Do Electric Cars Perform in the Cold Weather?
With the recent surplus of electric vehicles being created by manufactures, there are still a ton of questions revolving around the performance of the vehicles in various weather conditions. We know already that traditional gas engines can find themselves struggling to turn over once the temperature drops to a certain degree, mainly due to the cold cranking amps of the battery installed as well as if the engine is a combustion engine or fuel injected. Diesel-powered engines can suffer greatly as well, considering cold weather can effect glow plugs and other components within the engine needed to properly complete the start-up procedure. This raises questions as to how these newer electric cars actually perform in colder weather.
The Issues With Electronics and the Cold Weather
If you have ever found yourself entering your vehicle the day after a deep freeze, such as a snowstorm or cold front, you may notice your dash panel and head unit acting sluggish. This is usually seen by the almost melting effect occurring on your electronic devices. As more and more components are becoming touch screen, you may see these devices neglect to respond to your touch at all. But on vehicles that are primarily controlled by a touch screen, this could cause your vehicle to be temporarily unavailable; thus, not allowing you to turn on the defrosters or heating elements.
The Concern Surrounding Electric Cars
When it comes to electric cars, there is not a single manufacturer more popular than Tesla, a brand that has been known to make tall claims with varying results when it comes to electric powered vehicles. This has been highlighted in a video tweet “Tesla in winter conditions” that demonstrates their Model 3 vehicle drifting through a snowy tundra with ease, followed by a promotion that would allow you to take a trip to Finland to drive over a frozen lake in a Tesla Model 3. This is a marketing attempt to disparage the comments being made regarding the concerns of electric vehicles being unable to operate at a certain temperature. This coupled with the concerns over how long the vehicle can run and how long the battery will take to recharge.
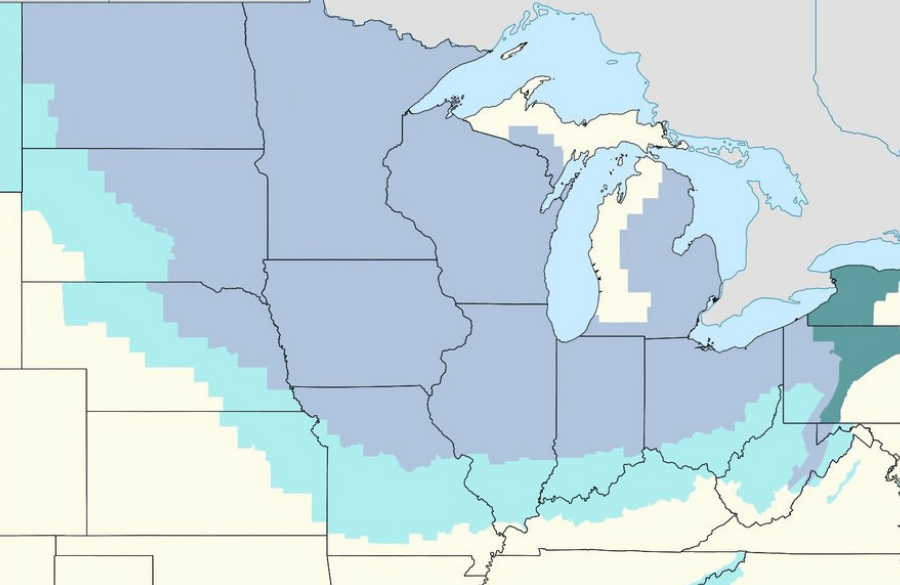
The main concerns have come out centering around the new Winter Storm Jaden that is entering the United States in the coming days, which is set to affect about 70% of the US population with sub-zero temperatures. Thanks to the Lithium-Ion batteries being used in these devices, there is uncertainty if the vehicles will continue to operate thanks to the temperature sensitivity of these components.
What are Lithium-Ion Batteries?
You may have heard the term lithium-ion battery being thrown around in topics centering around Smartphones, Laptops, and Tablets with varying results depending on the temperature and pressure. The most notable news regarding the dangers of lithium-ion batteries in high-pressure situations would come from the Galaxy Note 7, which was banned from all airlines due to explosions occurring under high pressure. Temperature issues are also noticeable in iPhones as well, with users experiencing temperature warnings at too high of heat and phones generally becoming unresponsive at lower temperatures causing them to shut down without warning.
To give a crash course in understanding how lithium-ion batteries work, the composition and operation of lithium-ion batteries rely on chemical reactions to operate and generate the power required to power your devices. When a lithium-ion battery is operating in normal temperatures, there is a constant firing of the ions inside the battery that generate the power needed to operate whatever device is being powered. When the battery drops in temperature these reactions slow depending on the surrounding temperature – causing the battery to provide less energy and provide inaccurate readings, or just shut down completely until the battery is warmed up. This could prove to be problematic in vehicles that cannot even start to begin the warming process and could, therefore, be rendered unusable until the surrounding temperature levels reach a stable temperature.
How This Affects Electric Cars
Thanks to the concerns over temperatures variations in batteries, a majority of electric car manufacturers are putting the diversity of the weather throughout the United States into account and are including thermal management systems inside of their own batteries. This will allow batteries to operate in the lowest of temperatures without causing internal damage. The challenge comes in the form of an electric engine vs. a standard combustion engine, with one being able to generate its own heat thanks to the kinetic energy provided from the gas-powered engine and the other purely relying on the Lithium-ion battery to start the engine. Even with the car powered on, the engine will be running at reduced power to run an onboard heater to warm the engine, which could prove to be troublesome on snow covered roads.
This cold could also drop the full range of the mileage provided by the car by about 20 miles, which is a large chunk on an already limited 265-mile range.
Tesla Supercharge Stations
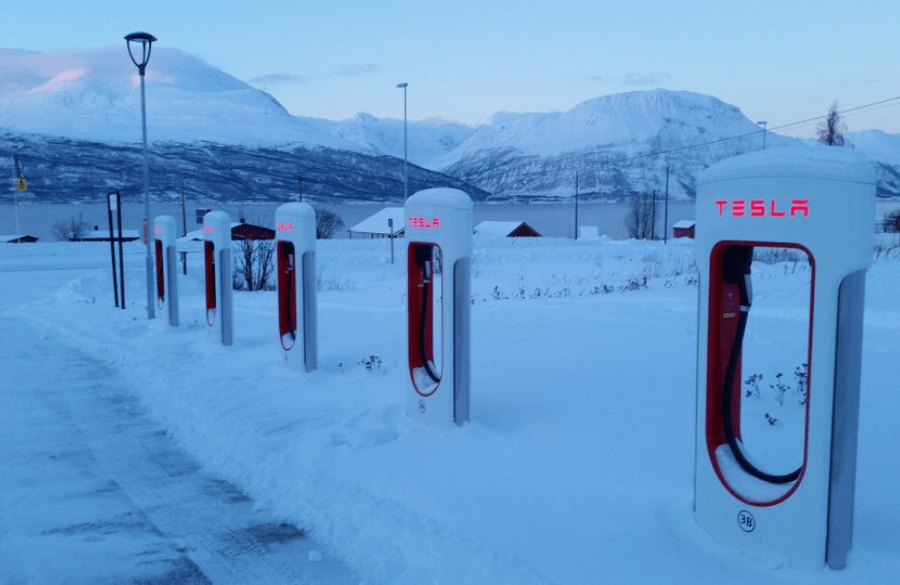

The picture above shows one of the northernmost Tesla supercharger stations on Earth, located in Norway, at a staggering -18°F. This proves the accessibility of the car in even the most arctic of tundra’s, but also emphasizes the struggle that accompanies charging your vehicle on the go. This is due to the average Tesla vehicle requiring an estimated 30 minutes to charge to full but will be severely limited in speed due to the battery limiting the amount of power intake to avoid damaging the battery. This means you will have to sit in the frozen weather while you wait for your vehicle to charge.
The Silver Lining
While all might seem “doom and gloom” on the topic of operating your electric vehicle in frozen weather, there are some methods that can be taken by current owners to get the most optimal amount of energy out of your vehicle’s battery. The first precaution to take, which also applies to your daily electronics, is to not allow the battery to drain too low (below 20%) to ensure that the vehicle can use that power to warm the vehicle before operating. With the advancements of Tesla’s and other smart car’s remote systems, warming the vehicle way before driving and removing from the power outlet will allow for the car to adjust and provide fewer issues when finally taking off.
With a ton of advancements in the works to optimize batteries for the cold, it’s likely one day there will be an overall solution to the issues of battery temperature. Until then, taking every precaution necessary will allow for less waste of energy and a longer lifecycle of the battery.
It also doesn’t hurt to brush up on how to take care of you car during winter, regardless of whether you drive an electrical vehicle or not. Understanding the most common issues and how to solve them can be life-saving when out on the road during the winter.


